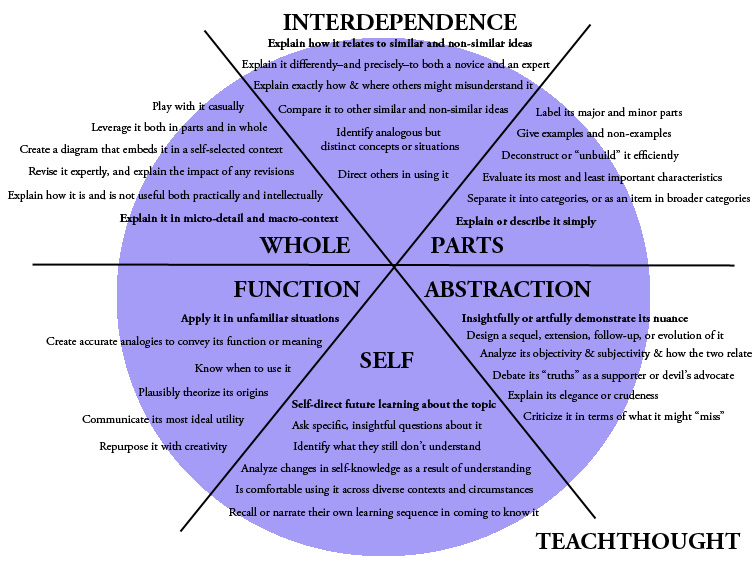


30 Universal Strategies For Learning Challenge something Make an observation Draw a conclusion Question something Revise a question based on observation & data Critique something Explain the significance Revise something Transfer a lesson or philosophical stance from one situation to another Improve a design Identify a cause and effect Compare and contrast two or more…

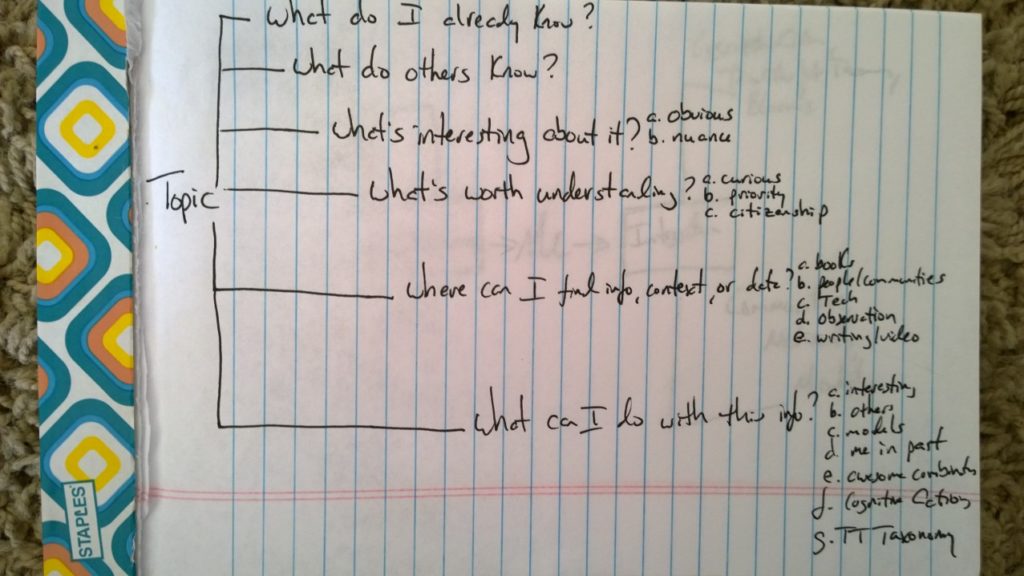
What I need to know What I know What others know What’s knowable What’s not knowable What’s most interesting What’s most important (see #1 and #2) How can/should I break this down into learnable bits and piees? Where should I start? How will I know I’ve learned? What should I do with what I learned?
27 Strategies For Learning Explain the significance Challenge something Draw a conclusion Form an important question Revise a question based on observation & data Critique something Observe something Revise something Transfer a lesson or philosophical stance from one situation to another Improve a design Identify a cause and effect Compare and contrast two or more…

Reading Competencies Idea 1. Identify and analyze a theme or thesis and its development (e.g, the use of supporting details, rhetorical techniques, literary devices, writing style, tone, mood, modalities, etc.) 2. Recognize how a theme or thesis or media fits into larger contexts (cultural, literary, digital, etc.) 3. Recognize and explain the features, nuance, history,…
50 Activities To Promote Digital Media Literacy In Students Infer the author’s purpose. Distinguish between primary and secondary audiences. Summarize the media by identifying its 3-5 most important ideas or events. Identify and diagram the literary elements (e.g., setting, characters, conflict, etc.) Identify and analyze characters as major or minor; flat or round; static or…